Introduction to Clavulanic Acid and Antibiotic Resistance
As a concerned individual, I've been following the issue of antibiotic resistance. It's a growing problem, and it poses a significant threat to public health. One compound that has emerged as a potential solution to this crisis is clavulanic acid. In this article, we will explore the challenges of antibiotic resistance and how clavulanic acid can play a vital role in addressing this issue.
The Rise of Antibiotic Resistance
Over the years, I've noticed that antibiotic resistance has become a significant concern worldwide. The misuse and overuse of antibiotics, along with the natural ability of bacteria to adapt, have led to the emergence of resistant strains. This resistance has made it increasingly difficult to treat infections, leading to longer hospital stays, higher medical costs, and increased mortality rates.
As a result, there is an urgent need for new antibiotics and strategies to combat bacterial infections, especially those caused by multi-drug resistant bacteria. This is where clavulanic acid comes into play as a potential solution to this growing problem.
Understanding Clavulanic Acid
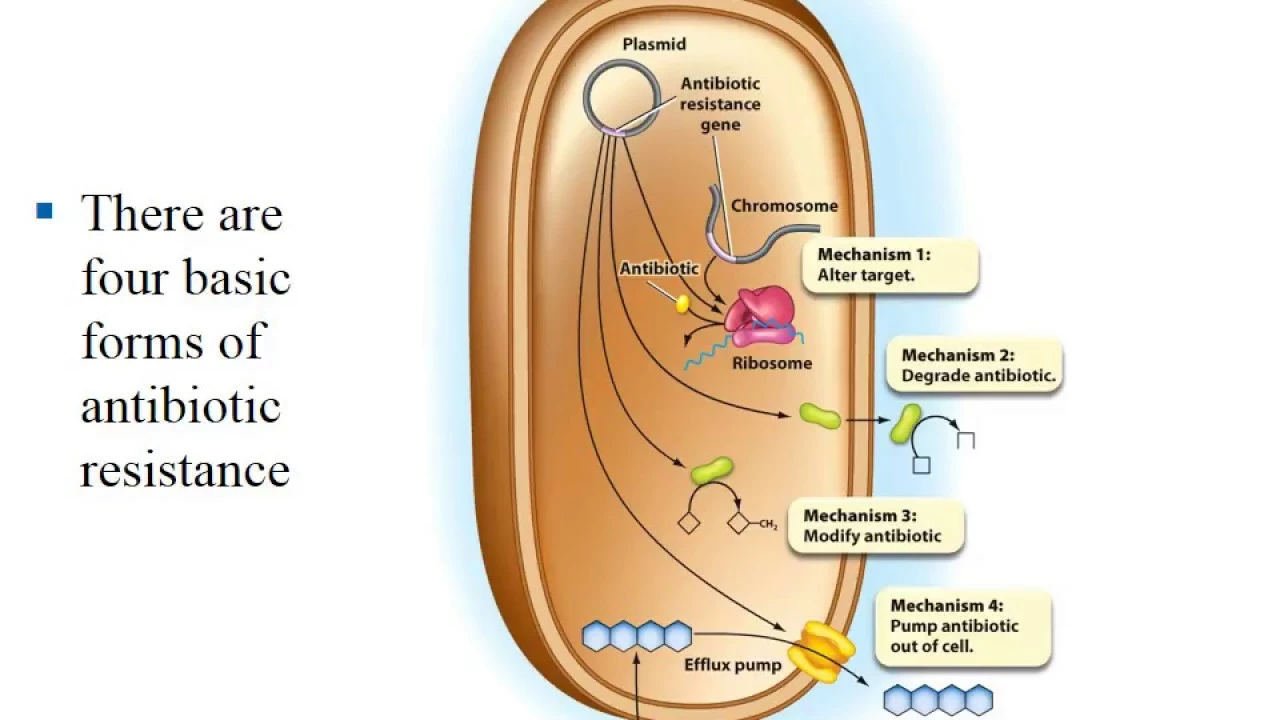
Clavulanic acid is a naturally occurring molecule derived from the bacterium Streptomyces clavuligerus. It is a β-lactamase inhibitor, which means it can block the action of enzymes called β-lactamases. These enzymes are produced by bacteria to break down and inactivate β-lactam antibiotics, such as penicillin and cephalosporins.
By inhibiting β-lactamases, clavulanic acid essentially protects the antibiotic from being degraded by the bacteria, allowing the antibiotic to effectively kill the bacteria. This makes clavulanic acid a valuable asset in the fight against antibiotic resistance.
Combating Resistance with Clavulanic Acid
One of the ways in which clavulanic acid is used to combat antibiotic resistance is by combining it with β-lactam antibiotics. The most well-known example of this is the combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid, which is commonly prescribed under the brand name Augmentin.
By combining the two, the effectiveness of the antibiotic is enhanced, and the chances of resistance developing are reduced. This combination has been proven to be highly effective in treating a wide range of infections, including respiratory, skin, and urinary tract infections.
Advancements in Clavulanic Acid Research
Over the years, I've been keeping an eye on the advancements in clavulanic acid research. Scientists are continually looking for ways to improve its effectiveness and expand its use in combating antibiotic resistance.
For instance, researchers are exploring the potential of combining clavulanic acid with other types of antibiotics or developing new β-lactamase inhibitors that can work alongside clavulanic acid. These efforts hold the promise of providing us with even more powerful tools to tackle antibiotic resistance.
Addressing the Challenges of Resistance Development
While clavulanic acid has proven to be a valuable weapon in the fight against antibiotic resistance, it is not without its challenges. One major concern is the possibility of bacteria developing resistance to clavulanic acid itself.
To mitigate this risk, researchers are focusing on understanding the mechanisms of resistance development and exploring strategies to prevent or overcome it. This includes studying the genetic mutations that lead to resistance and investigating new combinations of antibiotics and inhibitors that can bypass these resistance mechanisms.
Clavulanic Acid in Veterinary Medicine
As an animal lover, it's important to me that we also address the issue of antibiotic resistance in veterinary medicine. Just like in human medicine, clavulanic acid has been successfully used in combination with antibiotics to treat bacterial infections in animals.
However, it's crucial that we continue to research and develop new strategies to combat resistance in both humans and animals, as the two are interconnected, and resistance in one can impact the other.
Environmental Impact of Clavulanic Acid
As a responsible citizen, I'm concerned about the environmental impact of our actions. The production and use of antibiotics, including clavulanic acid, can have environmental consequences. For instance, antibiotic residues can enter water systems and soil, potentially contributing to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the environment.
Therefore, it's essential that we develop sustainable production methods and proper disposal techniques to minimize the environmental impact of clavulanic acid and other antibiotics.
Educating the Public on Antibiotic Use and Resistance
As a blogger, I believe it's essential to educate the public about antibiotic use and resistance. This includes promoting the responsible use of antibiotics, such as taking them only when prescribed and finishing the entire course of treatment, even when symptoms improve.
Furthermore, raising awareness about the importance of infection prevention measures, such as handwashing and vaccination, can help reduce the need for antibiotics and slow the development of resistance. Together, we can make a difference in the fight against antibiotic resistance and ensure a healthier future for all.
Conclusion: The Role of Clavulanic Acid in Addressing Antibiotic Resistance
In conclusion, clavulanic acid has emerged as a valuable tool in the fight against antibiotic resistance. By protecting β-lactam antibiotics from degradation by bacterial enzymes, it can help overcome resistance and improve treatment outcomes.
However, we must continue to invest in research and development to address the challenges associated with resistance, as well as educate the public on the responsible use of antibiotics. As we work together to tackle this issue, clavulanic acid will undoubtedly play a crucial role in addressing the challenges of antibiotic resistance.

Great overview of how clavulanic acid fits into the bigger fight against resistant bugs 😊. I love how you highlighted both the human and veterinary angles – it's so important to think holistically. The point about environmental residues really got me thinking about proper disposal. Keep spreading the word, every little bit helps!
Clavulanic acid is a must‑have tool in any modern antibiotic arsenal.
Nice job breaking down the science without drowning us in jargon. It's clear that combining clavulanic with amoxicillin makes a big difference in real‑world infections. Thanks for keeping it accessible!
Totally agree with the points you raised, especially about the environmental side. I've seen a few studies where runoff from farms actually spreads resistant genes, so disposal matters. Also, the synergy between clavulanic acid and β‑lactams is a clever workaround that buys us time. It's not a perfect solution, but it’s a solid step forward. Looking forward to more updates on greener production methods.
Ah, the melodrama of a single sentence, yet it reverberates like a lone violin in a symphonic battle.
In the grand tapestry of antimicrobial stewardship, clavulanic acid occupies a niche of undeniable significance. Its mechanism, whereby it irrevocably binds to the active site of β‑lactamases, exemplifies a biochemical elegance seldom observed in pharmacological adjuncts. By preserving the structural integrity of β‑lactam antibiotics, it extends the therapeutic window of agents that would otherwise be rendered inert. Moreover, the clinical evidence amassed over the past decades unequivocally demonstrates superior outcomes in infections ranging from otitis media to complicated urinary tract infections. The pharmacokinetic profile, characterized by a relatively short half‑life, necessitates careful dosing schedules to synchronize with its β‑lactam partner. Physicians, therefore, must remain vigilant in prescribing practices to avoid sub‑therapeutic exposure that could foster resistance. It is also pertinent to acknowledge that bacterial populations possess an astonishing capacity for genetic adaptation, which may eventually circumvent even the most robust inhibitors. Ongoing research into novel β‑lactamase inhibitors, such as avibactam and relebactam, seeks to complement or supersede clavulanic acid in the therapeutic arsenal. Yet, the economic realities of drug development impose constraints, making the repurposing and optimization of existing molecules an attractive strategy. Environmental stewardship, too, cannot be ignored; the dissemination of pharmaceutical residues into aquatic ecosystems demands rigorous waste‑management protocols. In this context, the development of biodegradable formulations of clavulanic acid could mitigate ecological impact while preserving clinical efficacy. While the specter of resistance looms, multidisciplinary collaboration between microbiologists, chemists, and clinicians offers a beacon of hope. Educational initiatives directed at both prescribers and patients remain paramount to curbing indiscriminate usage. In sum, clavulanic acid serves not merely as an adjunct but as a cornerstone in the contemporary fight against antimicrobial resistance. Its continued relevance will hinge upon judicious application, sustained research investment, and a collective commitment to responsible antibiotic stewardship.
I appreciate the way you highlighted accessibility; it really underscores the need for clear communication. It’s fascinating how a simple inhibitor can shift the entire treatment paradigm, and I’m hopeful we’ll see even more innovative combos soon. 🌱
We need to keep pushing for broader access to clavulanic‑based combos, especially in low‑resource settings where resistant infections are raging. The cost‑effectiveness of augmenting existing antibiotics is huge, and policymakers should take note. Let’s champion responsible usage while expanding availability.
The rhetoric around “miracle drugs” veils the gritty reality: bacteria evolve, period.
True, the science doesn’t care about hype its just survival of the fittest out there
Nice summary of the challenges
Indeed, the pharmacodynamic synergy between clavulanic acid and β‑lactams epitomizes a quintessential combinatorial strategy 🚀🔬.
Honestly, this whole “global coop” thing is a load of baloney – our own country should lead the charge, not rely on foreign pharma.
First, the premise is flawed: antibiotic resistance is a trans‑border issue that demands coordinated international policies, not isolationist rhetoric. Second, the data clearly show that collaboration accelerates development of inhibitors like clavulanic acid. Let’s base arguments on evidence, not nationalistic buzzwords.
Well‑written piece – the balance between scientific detail and public‑friendly language hits the mark.
Oh absolutely, because nothing says "engaging" like a perfectly balanced paragraph that reads like a textbook. Keep it up!
We must remember that our own health systems bear the brunt of misuse, so local regulation should trump any foreign guidelines.
You've raised a vital point about local stewardship, and I wholeheartedly agree – community‑level interventions can make a massive difference 🌍. By educating patients on proper antibiotic courses and ensuring pharmacies dispense only prescribed doses, we curb the selection pressure that fuels resistance. Coupled with monitoring programs that track resistance patterns regionally, we can adapt treatment guidelines swiftly. Let's also push for affordable access to clavulanic combos so that cost never becomes a barrier to proper care 😊. Together, a concerted effort will safeguard both present and future generations.
Great points! It's encouraging to see such proactive ideas, and I hope they inspire more initiatives in the near future.